Introduction to the Range Function in Python
The range function is a built-in Python function that generates a sequence of numbers. It is commonly used in loops and other scenarios where a series of numbers needs to be iterated. The range function provides a convenient way to generate sequences without explicitly creating a list of numbers. In this article, we will explore the range function in Python and learn how to use it effectively in different scenarios.
Syntax and Parameters
The syntax of the range function is as follows:
range(start, stop, step)
The range function accepts three parameters:
start(optional): The starting value of the sequence. If not specified, it defaults to 0.stop(required): The end value of the sequence (exclusive). Therangefunction will generate numbers up to, but not including, this value.step(optional): The step size or increment between numbers. If not specified, it defaults to 1.
Generating a Sequence of Numbers
Let’s start by looking at some examples of how to use the range function to generate a sequence of numbers.
Example 1: Basic Usage
for num in range(5):
print(num)
Output:
0
1
2
3
4
In this example, the range function generates a sequence of numbers from 0 to 4 (exclusive). The for loop iterates over each number and prints it.
Example 2: Specifying Start and Stop Values
for num in range(2, 8):
print(num)
Output:
2
3
4
5
6
7
In this example, the range function generates a sequence of numbers starting from 2 and ending at 7 (exclusive).
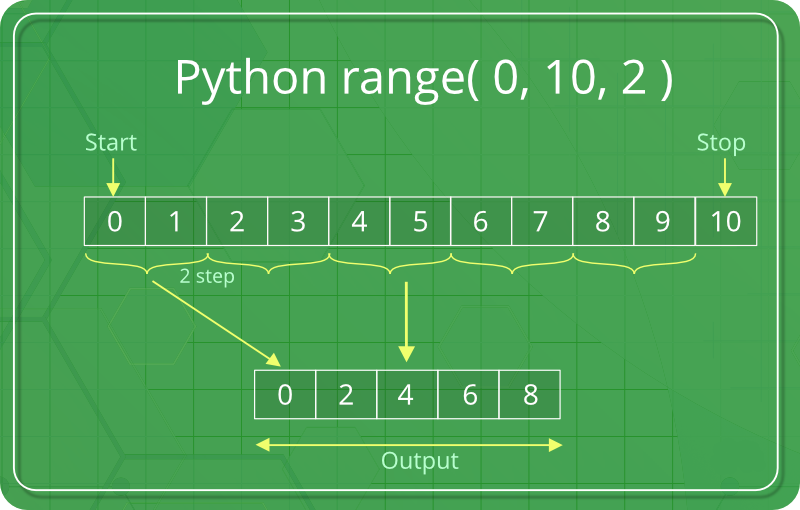
Example 3: Specifying a Step Size
for num in range(1, 10, 2):
print(num)
Output:
1
3
5
7
9
In this example, the range function generates a sequence of numbers starting from 1 and ending at 10 (exclusive) with a step size of 2.
Converting Range to List
Although the range function returns a sequence of numbers, it does not actually create a list. However, you can convert the range object to a list using the list function if you need to store the sequence in a list.
num_list = list(range(5))
print(num_list)
Output:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Common Applications
The range function is widely used in Python programming, particularly in scenarios where iterating over a sequence of numbers is required. Here are some common applications of the range function:
- Looping: The
rangefunction is commonly used inforloops to iterate over a specific range of numbers. - Indexing: The
rangefunction is useful for generating indices when iterating over a sequence or accessing elements in a list. - Creating Lists: By converting a
rangeobject to a list, you can create a list of numbers with a specified range and step size. - Controlled Iteration: The
rangefunction can be used to control the number of iterations in a loop by specifying the desired range.
Conclusion
The range function is a powerful tool in Python for generating sequences of numbers. By specifying the start, stop, and step values, you can create custom ranges and control the iteration process. The range function is commonly used in loops, indexing, and other scenarios where a series of numbers needs to be generated or iterated. Understanding how to use the range function effectively will enhance your ability to write efficient and concise Python code.

My name is Mark Stein and I am an author of technical articles at EasyTechh. I do the parsing, writing and publishing of articles on various IT topics.




+ There are no comments
Add yours